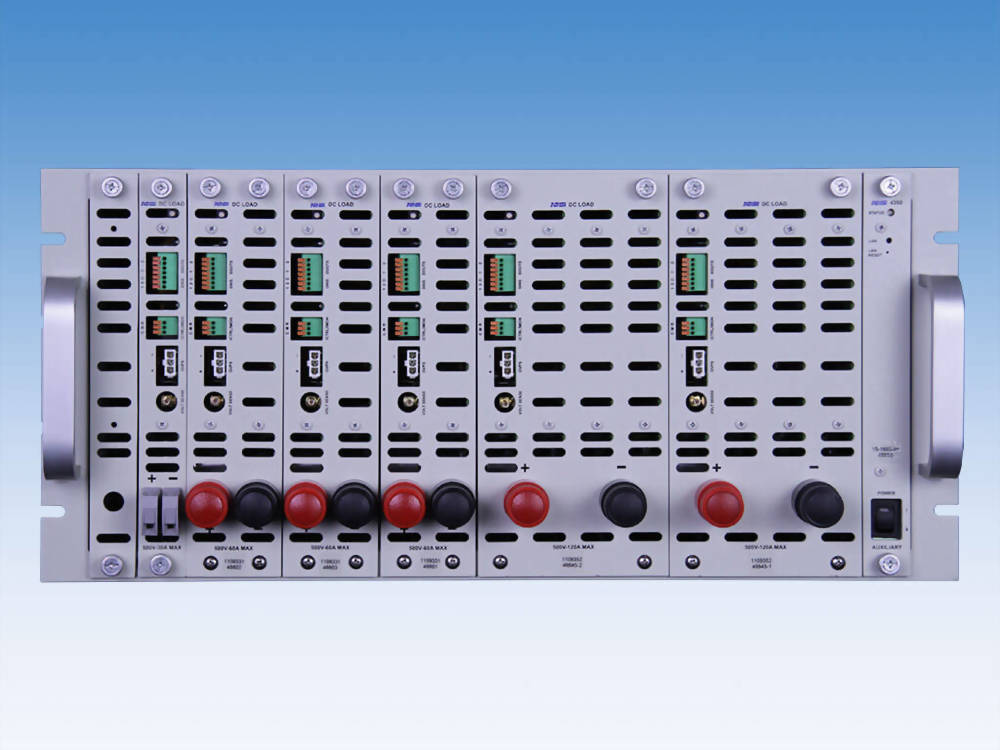
Modular DC Load 120V – 4312 Series
Modular DC Load for Charger Testing, LED Driver Testing, Solar Panel Testing, & More!
Features
-
3 sizes – 150, 300, & 600W @ 120V with advanced measurement capability built-in
-
Mix & match loads for maximum configuration flexibility
-
Up to 16 loads in a single, 8 3/4″ / 5U Model 4300 chassis
-
Front loaded & front connections
-
3 voltage and 3 current ranges for improved accuracy
-
High-resolution waveform capture for analysis of dynamic transients
-
Isolated digital inputs & outputs for test fixture support
-
PC/LAN control with LabVIEW & IVI drivers
Model 4312 Modular DC Load (120V) Specifications
|
Model #
|
4312-150
|
4312-300
|
4312-600
|
|
Chassis Slots
|
1
|
2
|
4
|
|
Power
|
150W
|
300W
|
600W
|
|
Voltage
|
0 – 120V
|
0 – 120V
|
0 – 120V
|
|
Current
|
0 – 40A
|
0 – 80A
|
0 – 150A
|
|
Physical
|
|
Mainframe Size (HxWxD)
|
8 3/4 x 19 x 22″/222 x 483 x 559mm
|
|
Weight
|
86lbs/39kg (fully loaded)
|
Advantages
-
Modular load maximizes configuration flexibility
-
Simplifies automated test stand development
– Triggerable set & measurment
– Short circuit mode & over voltage relay
– Isolated digital inputs & outputs
– Built-in SW watchdog & safety limits
-
Software tools to shorten test development time
– PC-based Softpanel GUI with scope display
– Supplied LabVIEW & IVI-C/IVI-COM drivers
– Optional: DC Load, emPower®, or Enerchron® test sequencer
Benefits
-
Modular – up to 16 loads or combinations in single chassis
-
Built in features require fewer test devices
-
Front connections simplify wiring
-
Safety limits protect UUT
Applications
The concept of having an advanced digital measurement system built in
to each load plus being able to combine up to 16 of such loads into a
single chassis opens several new test strategy possibilities that have
significant economic and quality benefits.
The most important test strategy is the ability to test consumer power devices such as chargers, adapters and LED drivers in parallel, up to 16 in a single pass. Test times for such devices are now measured in a few seconds.
The other major advantage of this distributed measurement is the
ability to test each output of a multi-output power conversion device
simultaneously rather than sequentially. Not only does this dramatically
reduce the overall test time but also provides far better
channel-to-channel performance measurements including dynamic cross
effects. In this manner quality of the devices tested takes a large step
forward because the parallel tester better simulates real life
conditions where all outputs are exercised together.
Yet another benefit of such a flexible load/measurement system is the
ability to reconfigure the loading to adapt to almost any new loading
arrangement required by brand new UUTs in the future.